EOS StainlessSteel 316L-4404
Material Data Sheet
EOS StainlessSteel 316L-4404
EOS StainlessSteel is a high-performance, marine-grade austenitic stainless steel that is molybdenum alloyed for enhanced corrosion resistance in chloride environments. 316L is a standard material for numerous applications in process, energy, paper, transportation, and other industries. EOS Stainless Steel 316L-4404 has a chemical composition corresponding to DIN EN 10088-3. All EOS StainlessSteel 316L parameter sets, including 40/80 µm, are compatible with EOS StainlessSteel 316L-4404 powder.
- High ductility and toughness
- High strength
- High corrosion resistance
- Chemical industry
- Food processing
- Water handling and marine applications
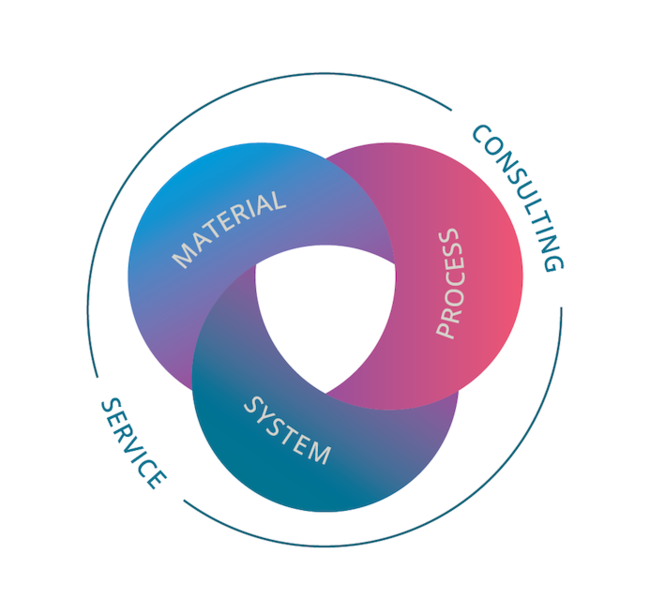
The EOS Quality Triangle
EOS incorporates these TRLs into the following two categories:
- Premium products (TRL 7-9): offer highly validated data, proven capability and reproducible part properties.
- Core products (TRL 3 and 5): enable early customer access to newest technology still under development and are therefore less mature with less data.
All of the data stated in this material data sheet is produced according to EOS Quality Management System and international standards
POWDER PROPERTIES
The chemical composition of EOS stainlessSteel 316L-4404 is in compliance with DIN EN 10088-3.
Powder Chemical Composition (wt.-%)
| Element | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|
| Fe | Balance | |
| Cr | 16.5 | 18.5 |
| Ni | 10.0 | 13.0 |
| Mo | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| C | - | 0.03 |
| N | - | 0.1 |
| Si | - | 1.0 |
| Mn | - | 2.0 |
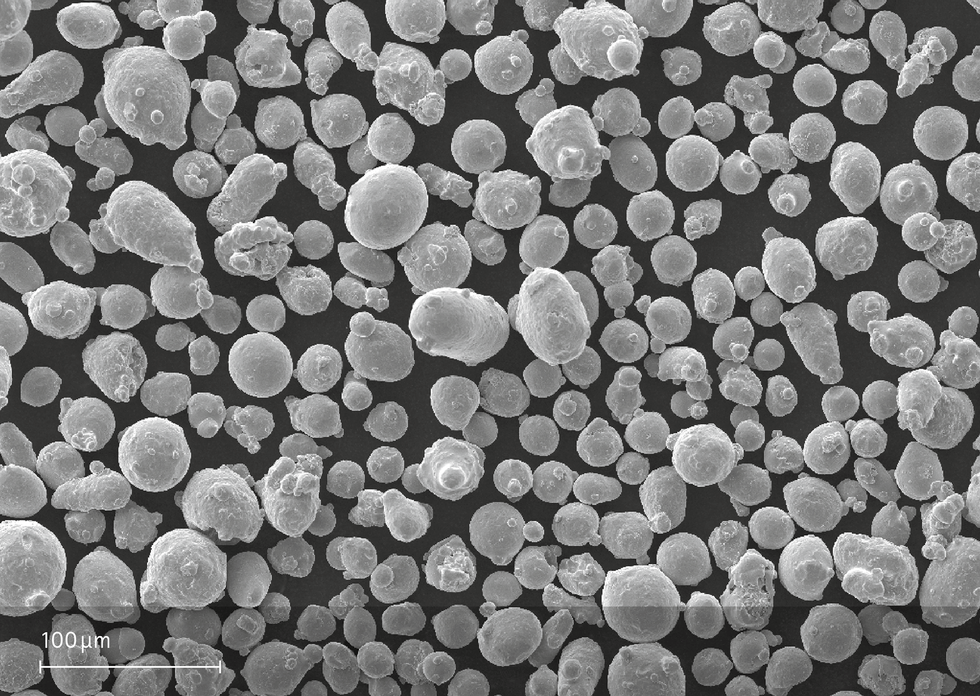
Powder Particle Size
| GENERIC PARTICLE SIZE DISTRIBUTION | 20 - 65 μm | |
|---|---|---|

HEAT TREATMENT
Optional according to DIN EN 10088-3
Stress relieve: Hold temperature 900 C, hold time minimum 2 h when throughly heated, water quenching or high speed gas quenching. Cooling rate to be high enough to prevent chromium carbide precipitation.
Solution annealing: Hold temperature 1100 C, hold time minimum 1,5 h when throughly heated, water quenching or high speed gas quenching. Cooling rate to be high enough to prevent chromium carbide precipitation.